AL REEM ISLAND STORWATER SYSTEM
Our Work Scope
We conducted modeling studies to design the transport and dilution of the stormwater discharge to seawater to the north of the island. The main objectives of the study are:
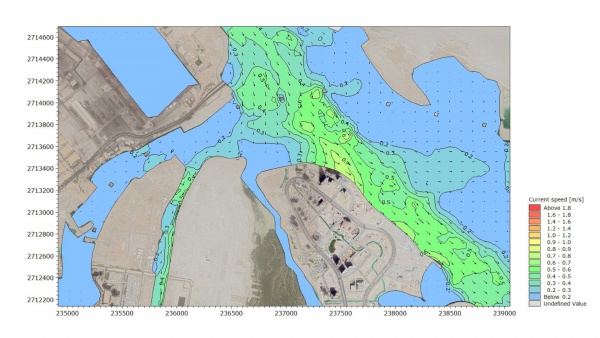
- To prepare a hydrodynamic model of the water network around the project site to determine the current regime,
- Carrying out advection-dispersion model simulations to identify the affected areas from stormwater discharge
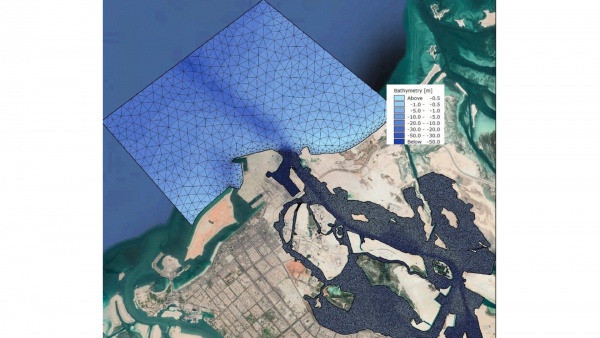
Hydrodynamic Model
All the modeling work has been carried out in-house by ARTI Proje adopting advanced numerical modeling software MIKE21 of DHI which comprises various modules.
The modeling approach, which started on a large scale for the whole gulf area, was then applied on a small scale to capture finer details of the project site. This cascaded approach provided accurate simulation for the engineers.
Taking care that the current regime being directly influenced by offshore water level conditions and tidal variations, we run simulations for various seasonal conditions.
Al Reem Island is located in the middle peninsula between Al Maryah Island and Shams Abu Dhabi. The project area is surrounded by a water network consisting of both artificial and man-made canals. The storm outfall structure draining from the canals will be constructed at the north-western edge of the peninsula.
ARTI Proje provided engineering and consulting services with the aid of numerical modeling to investigate the impact of stormwater marine discharge.
Client: Blue Sea Consultants Est.
Advection-Dispersion Model
Model tests of advection-dispersion were conducted by using the software MIKE21's special module to simulate the dilution of the discharged water.
With defining initial conditions over the model area that is the same as the hydrodynamic model, the variations in oil concentration and transport direction were determined by advection-dispersion modeling. Model tests were conducted considering mainly two cases:
- Stormwater discharge during tidal flooding
- Stormwater discharge during tidal ebbing